🙋♀️ TensorFlow Sequential API와 Functional API를 사용해 모델 구조를 만들고 학습하기
0. Sequential vs Functional API
Sequential API
- 레이어의 흐름이 순차적인 경우 사용 (layer-by-layer)
- 텐서가 이전 레이어에서 다음 레이어로 바로 이어질 때에 사용 가능
Functional API
- Sequential API보다 유연한 API로 다음의 기능을 사용할 수 있음
- 여러 개의 input을 받거나 여러 개의 output을 내야 하는 경우
- Layer을 공유하는 경우 (샴 네트워크 등....)
- Residual Network 구현
1. 태스크 이해하기 : MNIST 데이터 분류
- 손으로 쓴 0-9 사이의 숫자 이미지를 인풋으로 받아 숫자를 추론하는 태스크
- 60,000장의 학습 이미지와 10,000장의 테스트 이미지 존재
- 각각의 이미지는 28x28 사이즈의 흑백 (1-channel) 이미지
# MNIST 데이터셋 다운로드
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.02. 아키텍처 선택하기
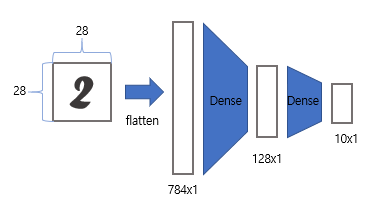
모델
- 28x28 2차원의 이미지를 784x1차원 벡터로 변환
- Fully Connected Layer을 사용해 128차원 벡터로 정보 압축
- 최종적으로 0~9 중의 하나의 카테고리로 매핑하는 Fully Connected Layer 연결
Loss
- Sparse Categorical Cross-entropy Loss를 사용해 학습
Metric
- Accuracy 트래킹
Callback
- Early Stopping Callback 사용
3. Sequential API를 활용하여 모델 학습하기
3-1) 모델 레이어 쌓고 컴파일하기
- model.compile에서는 optimizer, loss, metric을 정의
# Layer 쌓기
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
# 모델 컴파일하기
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()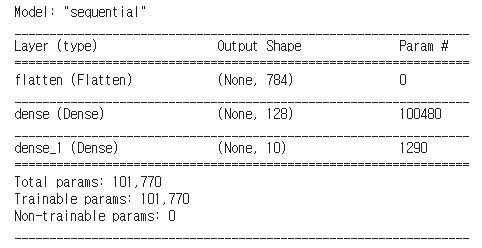
3-2) 모델 학습하기
- model.fit을 통해 실제 데이터를 사용해 모델을 학습
- 이때 callbacks를 통해 학습 사이클에서 수행할 작업을 정의할 수 있음
# EarlyStopping Callback 정의하기
callback = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss', min_delta=0, patience=1, verbose=0,
mode='auto', baseline=None, restore_best_weights=False
)
# Model.fit을 통해 학습하기
model.fit(
x=x_train, y=y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=50, verbose=1,
callbacks=callback, validation_split=0.2)

4. Functional API를 활용하여 모델 학습하기
4-1) 모델 레이어 쌓고 컴파일하기
# Input Layer 정의하기
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(28,28,))
# Input ~ Output 연결하기
x = tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28))(inputs)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu')(x)
outputs= tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(x)
# tf.keras.Model을 사용해 인풋 ~ 아웃풋 연결하기
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
# 모델 컴파일하기
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()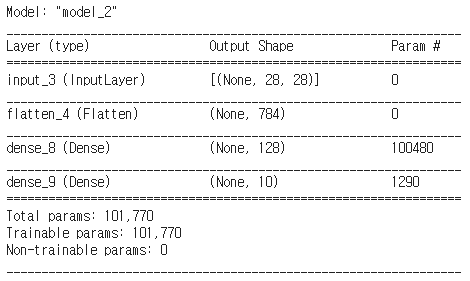
4-2) 모델 학습하기
# EarlyStopping Callback 정의하기
callback = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss', min_delta=0, patience=1, verbose=0,
mode='auto', baseline=None, restore_best_weights=False
)
# Model.fit을 통해 학습하기
model.fit(
x=x_train, y=y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=50, verbose=1,
callbacks=callback, validation_split=0.2)
참고 자료: https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/quickstart/beginner

'코딩' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [TensorFlow] Vision Modeling(2) Transfer Learning (0) | 2021.06.27 |
|---|---|
| [TensorFlow] Vision Modeling(1) MNIST 태스크 모델링하기 (2) | 2021.06.06 |
| [2021 Hackathon] 2. Modeling (0) | 2021.01.31 |
| [2021 Hackathon] 1. Data Preprocessing (1) | 2021.01.29 |
| [Python] IR 검색 알고리즘 - BM25 / 엘라스틱서치 랭킹 알고리즘 / 파이썬 rank_bm25 모듈로 문서 검색 구현하기 (0) | 2020.03.01 |

